 A device that serves as an input source of currents and voltages from an electric power system to instruments, relays, meters, and control devices. The basic design is that of a transformer with the primary winding connected to the power system, and the secondary winding to the sensing and measuring equipment.more....
A device that serves as an input source of currents and voltages from an electric power system to instruments, relays, meters, and control devices. The basic design is that of a transformer with the primary winding connected to the power system, and the secondary winding to the sensing and measuring equipment.more....
Senin, 22 Desember 2008
Transformer
 A device that serves as an input source of currents and voltages from an electric power system to instruments, relays, meters, and control devices. The basic design is that of a transformer with the primary winding connected to the power system, and the secondary winding to the sensing and measuring equipment.more....
A device that serves as an input source of currents and voltages from an electric power system to instruments, relays, meters, and control devices. The basic design is that of a transformer with the primary winding connected to the power system, and the secondary winding to the sensing and measuring equipment.more....
Alternating current (AC)
 Electric current that reverses direction periodically, usually many times per second. Electrical energy is ordinarily generated by a public or a private utility organization and provided to a customer, whether industrial or domestic, as alternating current.more..
Electric current that reverses direction periodically, usually many times per second. Electrical energy is ordinarily generated by a public or a private utility organization and provided to a customer, whether industrial or domestic, as alternating current.more..Kamis, 18 Desember 2008
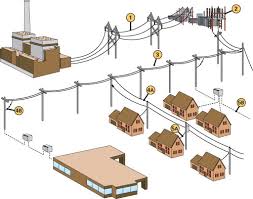
Transmission Substation
 The three-phase power leaves the generator and enters a transmission substation at the power plant. This substation uses large transformers to convert the generator's voltage (which is at the thousands of volts level) up to extremely high voltages for long-distance transmission on the transmission grid.more....
The three-phase power leaves the generator and enters a transmission substation at the power plant. This substation uses large transformers to convert the generator's voltage (which is at the thousands of volts level) up to extremely high voltages for long-distance transmission on the transmission grid.more....Power Cable
 A power cable is an assembly of two or more electrical conductors, usually held together with an overall sheath. The assembly is used for transmission of electrical power. Power cables may be installed as permanent wiring within buildings, buried in the ground, run overhead, or exposed. Flexible power cables are used for portable devices, mobile tools and machinery.more....
A power cable is an assembly of two or more electrical conductors, usually held together with an overall sheath. The assembly is used for transmission of electrical power. Power cables may be installed as permanent wiring within buildings, buried in the ground, run overhead, or exposed. Flexible power cables are used for portable devices, mobile tools and machinery.more....
Rabu, 17 Desember 2008
The Indonesia Power Grid
 Indonesia needs to spend about $27 billion on new plants and power lines by 2012 to meet.....
Indonesia needs to spend about $27 billion on new plants and power lines by 2012 to meet.....
Selasa, 16 Desember 2008
POWER FACTOR

The majority of electronics designers do not worry about Power Factor (PF); PF is
something that you learnt one day at school in your “electrotechnics course” as being
the cos of j, the phase angle between the voltage and current waveforms.more...
something that you learnt one day at school in your “electrotechnics course” as being
the cos of j, the phase angle between the voltage and current waveforms.more...
Senin, 15 Desember 2008
Electric Power Plants
Electric Power Plants have a number of components in common and are an interesting study in the various forms and changes of energy necessary to produce electricity.more...
Jumat, 12 Desember 2008
Safety and Health Topics Electric
 Electric power generation, distribution, and transmission hazards are addressed in specific standards for the construction industry. This section highlights OSHA standards, the Regulatory Agenda (a list of actions being taken with regard to OSHA standards), and directives (instructions for compliance officers) and standard interpretations (official letters of interpretation of the standards) related to power transmission and distribution in the construction industry. More....
Electric power generation, distribution, and transmission hazards are addressed in specific standards for the construction industry. This section highlights OSHA standards, the Regulatory Agenda (a list of actions being taken with regard to OSHA standards), and directives (instructions for compliance officers) and standard interpretations (official letters of interpretation of the standards) related to power transmission and distribution in the construction industry. More....
Electric Generation

Electric Generation
The electricity generation sequence involves taking charge from the Earth, doing work on it to give it energy (expressed in terms of voltage), transporting the energy via a distribution system, using the energy, and dumping the spent charge back to the Earth. The Earth acts as a charge reservoir and reference potential for the energy transfer process. More.....
The electricity generation sequence involves taking charge from the Earth, doing work on it to give it energy (expressed in terms of voltage), transporting the energy via a distribution system, using the energy, and dumping the spent charge back to the Earth. The Earth acts as a charge reservoir and reference potential for the energy transfer process. More.....
Selasa, 09 Desember 2008
Two phase electrical power

Two-phase electrical power was an early 20th century polyphase alternating current electric power distribution system. Two circuits were used, with voltage phases differing by 90 degrees. Usually circuits used four wires, two for each phase. Less frequently, three wires were used, with a common wire with a larger-diameter conductor. Some early two-phase generators had two complete rotor and field assemblies, with windings physically offset by 90 electrical degrees to provide two-phase power. The generators at Niagara Falls installed in 1895 were the largest generators in the world at the time and were two-phase machines.more....
Single-phase electric power
 In electrical engineering, single-phase electric power refers to the distribution of alternating current electric power using a system in which all the voltages of the supply vary in unison. Single-phase distribution is used when loads are mostly lighting and heating, with few large electric motors. A single-phase supply connected to an alternating current electric motor does not produce a revolving magnetic field; single-phase motors need additional circuits for starting, and such motors are uncommon above 10 or 20 kW in rating.more......
In electrical engineering, single-phase electric power refers to the distribution of alternating current electric power using a system in which all the voltages of the supply vary in unison. Single-phase distribution is used when loads are mostly lighting and heating, with few large electric motors. A single-phase supply connected to an alternating current electric motor does not produce a revolving magnetic field; single-phase motors need additional circuits for starting, and such motors are uncommon above 10 or 20 kW in rating.more......
Electricity Distribution

There are many special challenges in maintaining the electricity distribution network in our area. The geography means that we are sometimes subject to some of the most punishing weather conditions in the Indonesi. Whether we are dealing with gale force winds which frequently batter the South West and West Wales coasts, the problems caused by salt corrosion along the coastline, or the fact that Devon, Cornwall and Pembrokeshire's population can double during the holiday season, WPD is committed to providing a reliable electricity supply and constantly strives to improve the service we give our customers.more
Kamis, 04 Desember 2008
Battery Voltage
The battery voltage level used in most of the small and medium power rated UPS will be of low value compared to the d.c voltage required to synthesize sine wave output of 230V r.m.s value by SPWM without using a level shifting transformer. The battery level is 12-24V up to 1kVA rating, in the 36-48V rating up to 3kVA and 120V for rating up to 10kVA.It is true that many manufacturers have started employing 360V battery even in the rating range of 500VA to 10kVA.But there are definite advantages in using as low a battery voltage as the current power semiconductor technology permits from the point of view of battery life and better reliability from UPS.more...
Electronic Shooping

Electronic Shopping Many Indonesians were still believing that products that in marketed overseas his quality was far more better than products that in marketed in the country. Around them many that were deliberate went overseas only a to shop. You some among them?
Electrical Power

Electric power is defined as the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.
Electrical power is distributed via cables and electricity pylons like these in Brisbane, Australia.
When electric current flows in a circuit, it can transfer energy to do mechanical or thermodynamic work. Devices convert electrical energy into many useful forms, such as heat (electric heaters), light (light bulbs), motion (electric motors), sound (loudspeaker) or chemical changes. Electricity can be produced mechanically by generation, or chemically, or by direct conversion from light in photovoltaic cells, also it can be stored chemically in batteries.
Electrical power is distributed via cables and electricity pylons like these in Brisbane, Australia.
When electric current flows in a circuit, it can transfer energy to do mechanical or thermodynamic work. Devices convert electrical energy into many useful forms, such as heat (electric heaters), light (light bulbs), motion (electric motors), sound (loudspeaker) or chemical changes. Electricity can be produced mechanically by generation, or chemically, or by direct conversion from light in photovoltaic cells, also it can be stored chemically in batteries.
Langganan:
Postingan (Atom)
